hyperDENT job name
|
Original job name predefined by hyperDENT.
|
Jobname
|
Displayed in the job list, can be freely edited, preferably in accordance with the operational step and cycle, e.g.: “Roughing cavity.”
|
Calculate
|
|
Yes
|
Calculate the job.
|
No
|
Disable calculation; the job remains in the list but is not included in the calculation.
|
Calculate if
|
Conditional calculation. This means you can calculate two jobs that are the same depending on the groove depth of tools of different lengths.
|
|
▪Shorter tools are more suitable for small groove depths. They are more stable and produce better surfaces, greater accuracy, and chipping performance, but they cannot be used for larger groove depths because of the risk of collision and due to insufficient length. ▪Longer tools are needed for bigger groove depths in order to reach the required depth.
Examples “Calculate if”
|
Off
|
Calculation is always performed, e.g., for a single tool length.
|
Groove depth bigger
|
Calculation is only performed when the groove depth is bigger than the default value, e.g., for the longer tool.
|
Groove depth smaller
|
Calculation is only performed when the groove depth is smaller than the default value, e.g., for the shorter tool.
|
Caution! Use tools with the same diameter and the same allowance.
|
Groove depth
|
Value from the top of the blank.
Reference plane for conditional calculation.
|
Bottom of blank
|
|
Mid of blank
|
|
Value from the top of the blank.
|
The Z-level to the depth limit is generated parallel to the blank.
|
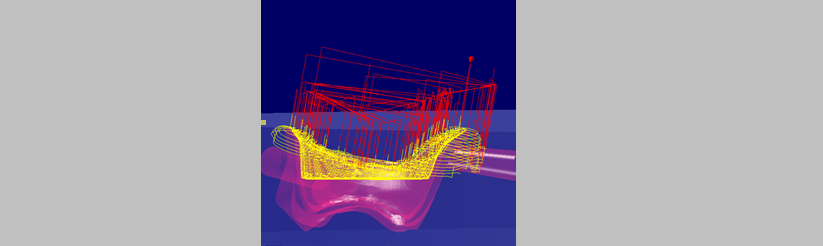
|
Value from top of machining area
|
“Top of machining area” refers to the highest point of the machined areas.
The Z-level to the depth limit is generated perpendicular to the machining direction.
|
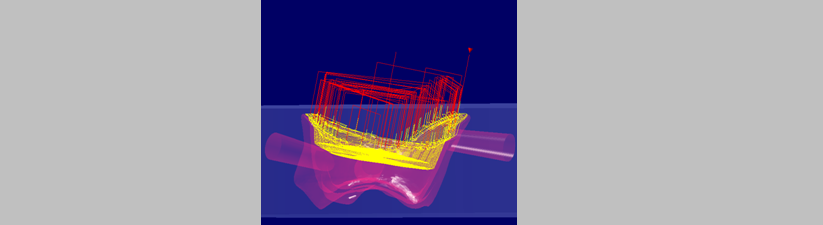
|
Depth value
|
Groove depth in mm from the top of the blank or the machining area.
|
Strategy
|
Cycle for machining. Selection window with a list of the available cycles.
|
|
|
Checking the milling boundary
|
When producing the dental restoration, the material must be removed in a sufficiently large area (milling area) around the part so that the tool can machine all areas of the part.
The milling boundary determines the width of the milling area and is dependent on:
the tool diameter,
the inclination for tilted machining, and
the inclination for coping-specific tilted machining.
Using the boundary check, hyperDENT can determine before the calculation whether the milling boundaries are large enough for the current machining process. This helps to prevent aborted calculations and incorrect machining.
|
|
|
Non-tilted machining
|
No automatic widening of the milling boundaries in the case of a main machining direction without tilting and orthogonal alignment of the part to the blank.
|
If necessary, the milling boundaries must be manually extended, e.g., if a tool with a widened shank and short tip would collide with the blank for a large groove depth.
|
|
|
Tilted machining
|
For tilted machining with active boundary check, a check is performed to establish whether the milling boundaries are large enough for the current machining process. If necessary, the milling boundaries are extended automatically.
When you enable the “Tool tip” setting, the milling boundary is only extended according to the diameter of the tool tip; the tool shank is not checked.
If tools with a larger shank diameter are used at greater depths, a collision message is issued if the collision check is activated; otherwise, there a collision between the tool shank and the blank will occur.
|
Boundary check
|
Check (default for tilted machining) to establish whether the milling boundaries are large enough for the current machining process. If not, a message is issued and the milling boundary must either be extended or, in the case of tilted machining, it is extended automatically.
|
Off
|
No check. A collision message may be issued if the collision check is activated; otherwise, a collision might occur or unmachined areas may result.
|
Tool tip
|
Only the tool tip is checked. For tools with a widened shank and short tip, a collision message is issued if the collision check is enabled; otherwise, there a collision with the blank will occur for a large groove depth.
|
Shank
|
The tool shank is checked and can be immersed in the blank. Larger milling area boundaries result in higher material consumption and longer machining times. Older templates are automatically set to the “Shank” for safety reasons.
|
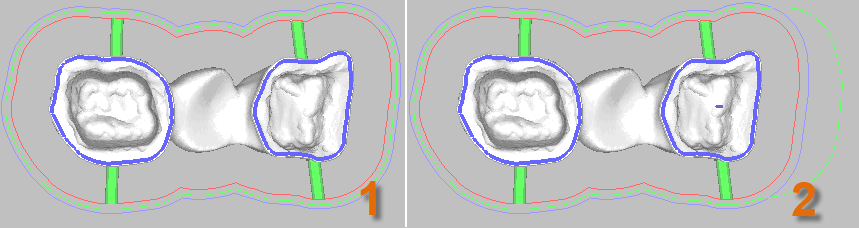
1) Milling boundary
2) Enlarged milling boundary to account for a large tilt
If a collision is detected when the milling boundaries for tilted machining are checked, the program will automatically extend the milling boundary (2).
Errors may occur in rare cases if the tilt angle is very large.
|
Caution! Configure the check carefully to avoid the risk of collision. For a very large machining depth and short tool tip length, use the tool shank check.
|
Examples for “Boundary check”
|
|
Tool
|
Tool for this job; selection menu with a list of preconfigured tools.
|
Spindlespeed
|
Spindle speed of the tool in rotations/min. Follow the instructions of the machine manufacturer (maximum spindle speed).
|
Feedrate (mm/min)
|
The speed at which the tool progresses along the calculated paths.
Follow the instructions of the machine manufacturer (maximum feedrate).
|
Feedrate axial (mm/min)
|
The speed at which the tool progresses along the calculated paths in Z-direction.
Follow the instructions of the machine manufacturer (maximum feedrate).
|
Reduce feedrate on fullcut
|
Reduce the feedrate to protect the tools when processing material that is difficult to cut. Can result in an extended calculation and machining time.
|
Max. groove depth
|
Depth limit of the toolpath for a job according to the tool length.
|
Unlimited
|
No depth limit.
|
Bottom of blank
|
|
Mid of blank
|
|
Value from the top of the blank.
|
The Z-level to the depth limit is generated parallel to the blank.
|

|
Value from top of machining area
|
“Top of machining area” refers to the highest point of the machined areas.
The Z-level to the depth limit is generated perpendicular to the machining direction.
|

|
Depth value
|
Maximum groove depth in mm, from the top of the blank or machining area.
|
Use cap specific directions
|
Details of the rotation axis for coping-specific tilting.
If the machining direction is not determined by the CAD, you can configure set it in the context menu: --> “Set milling direction” > “Coping-specific alignment.”
|
No
|
No coping-specific alignment/tilting.
|
X+Y rotation
|
Rotation axes for 5X machines.
|
X rotation
|
X rotation axis for 3+1 machines.
|
Y rotation
|
Y rotation axis for 3+1 machines.
|
Allowance
|
Remaining material (in mm) that should be left over on the part surface after this stage for further machining (finishing, fine finishing).
|
Step down
|
Maximum infeed distance in mm in Z-direction. Corresponds to the clearance of the machining planes and determines their number:
|
Single plane
|
Step down > (surface – depth)
|
Multiple planes
|
Step down < (surface – depth)
|
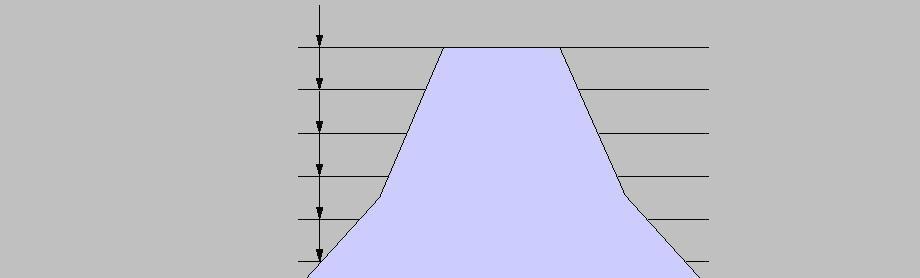
|
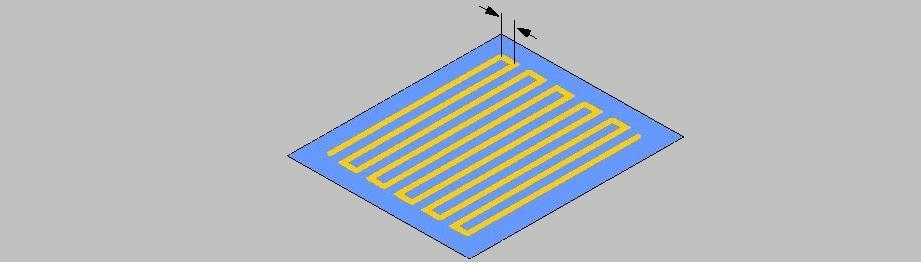
Step factor
|
Tool diameter factor for the maximum horizontal infeed of the tool:
“0.5” corresponds to an infeed of 50% of the mill diameter.
|
|
Fillet corners
|
Internal corners are rounded for all roughing and rest machining jobs to protect the tool when working with hard materials.
The machining tolerance is ignored in this case, which increases the calculation time.
|
Plunge strategy
|
|
Ramp/Helix
|
Method employed by the tool to plunge into the material in Z-direction.
|
Planar mode
|
Method employed by the tool to machine the material in Z-direction.
|
Optimized in
|
Machining from the outside to the inside.
|
Inside out
|
Machining from the inside to the outside.
|
Ramps/Helix angle
|
Angle in degrees with which the tool plunges into the material in Z-direction:
“90” corresponds to a direct infeed in
Z-direction.
|
Skip small pockets
|
|
Yes
|
Skip pockets; do not machine.
|
No
|
Machine pockets and position close to the tool diameter only when processing very narrow coping areas.
|
Collision check
|
Includes the tool or tool and holder in the calculation.
|
Tool only
|
Collision check for the tool only.
|
Tool and holder
|
Collision check for tool and tool holder.
|
Off
|
No collision check; quicker calculation.
Only for non-critical parts.
|
Avoid collision
|
|
Yes
|
The calculation is not canceled if there is a collision, but alternative milling paths are determined autonomously in the cycle.
|
No
|
Disable “Avoid collision” to reduce the calculation time.
|
Machining tolerance
|
Deviation (resolution) in mm when calculating the toolpaths.
In a template (job list for full machining), where possible only common values should be used as the calculation time increases if there are many different values.
For example, one value for roughing cycles and a second one for finishing cycles would be ideal.
|
Blank tolerance
|
Resolution of blank tracking in mm.
For material that is difficult to cut, you should set a finer resolution.
|
Comment
|
Comments that are listed for a specific job in the NC code. This can be parameters or simple text input.
Available parameters:
|
[JOBNAME]
[STOCKNAME]
[BLANKEXTERNALID]
[BLANKCHARGE]
[BLANKTYPENAME]
[IS_SINGLEUNITBLANK]
[IS_PREFAB]
[BLANKHEIGHT]
[BLANKWIDTH]
[BLANKDEPTH]
[MATERIALNAME]
[TPLENGTHFACTOR]
[MACHINENAME]
[FIXTURENAME]
[FIXTUREINSTANCE]
[SLOTNAME]
[PARTNAME]
[PATHTOMODEL]
[MODELNAME]
|
Name of the job
Designation of the blank
External ID of the blank defined by the user
Batch number (LOT) of the blank
Designation of the blank type
Flag for identifying a single-element blank
Flag for identifying a preform blank
Height of the blank
Width of the blank
Depth of the blank
Designation of the material
Material-specific length factor for toolpaths
Designation of the machine
Designation of the holder
Name of the holder instance
Designation of the slot in the holder
Name of the part
File path of the STL model
File name of the STL file
|
NC text before tool change
NC text after tool change
NC text before first position
NC text after first position
NC text after last position
|
Enter free text modules (job-specific NC data) such as control instructions, etc.
|
Caution! Risk of collision! hyperDENT does not perform a syntax or collision check of the NC texts entered. Only use this function if the machine being used can evaluate the data correctly.
|
\n
|
Separator for multi-line instructions in the
NC program (line break).
Example of multi-line instruction:
NC text input H123=28\nH124=4\nM22
Output
H123=28
H124=4
M22
|